Źródło: Arduino to ESP8266 Data With Serial Communication Using Arduino IDE
Transmisja Szeregowa (Serial Communication) to łatwy sposób na rozszerzenie możliwości współpracy ESP8266 z większą ilością czujników, nRF24, wyświetlaczy itp. Albo też rozszerzenie możliwości dowolnej płytki Arduino o moduł sieciowy ESP8266. Jak zwykle ACROBOTIC wykonało świetną robotę, dodatkowo posługując się formatem Json przy przesyłaniu danych.
W DynamicJsonDocument() należy podać wielkość pamięci dynamicznej, która pomieści naszą strukturę. Przydatny jest do tego kalkulator:
Pamiętać trzeba żeby wpisać właściwą formę naszej struktury Json
{
"type": "response",
"light": 200,
"temp": -50.3,
"hum": 100.0
}
ACROBIOTIC
O kilku rzeczach trzeba tu pamiętać:
- Po pierwsze konieczne jest zainstalowanie biblioteki ArduinoJson w wersji 6+. Wersje starsze nie będą działać.
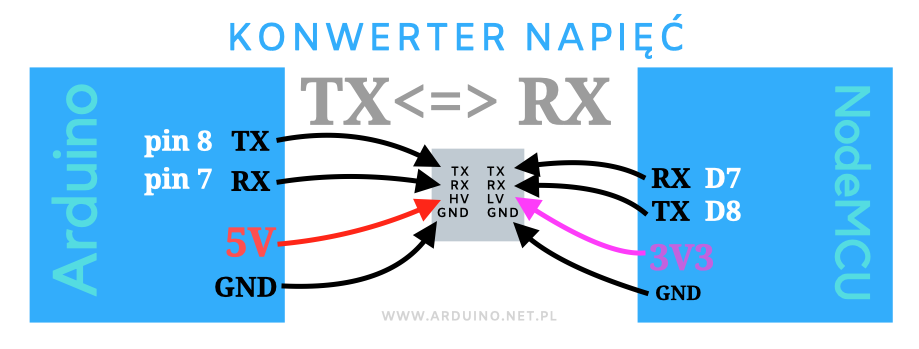
- Po drugie nie wolno łączyć TX z RX obu płytek przed załadowaniem programów. U mnie powodowało to przedziwne informacje o errorach. Jeśli mamy podłączone inne płytki przez USB, które wysyłają informacje przez Serial, też lepiej je odłączyć przy wysyłaniu skeczy.
- Pamiętać też należy aby połączyć komputer z siecią WiFi zanim wpiszemy numer strony na którym wyświetlają się dane. Ja zapomniałem, bo mam sieć na kablu i było trochę nerwów.
Tak łączymy platformy:
TX <-> RX
RX <-> TX
LINKI
- HOW TO SERIAL COMMUNICATION BETWEEN NODE MCU AND ARDUINO
- https://github.com/yarogniew/serial_connection/tree/master/Serial_dwie_strony/
- Arduino : Connecting Arduino UNO with ESP8266 / bardzo prosty sposób komunikacji
- Arduino dokumentacja: Serial
- arduinojson.org
- #152 Additional ESP32 Serial Channels in Arduino IDE (Quickie) by Andreas Spiess
Źródło: Arduino : Connecting Arduino UNO with ESP8266
Proste połączenie Arduino z ESP8266 przez serial (łączymy D3 Arduino z RX NodeMCU8266), wykorzystujące format Json, ale bez biblioteki. Płytki połączyłem przez moduł obniżający napięcie, ale można też bez, podobno ESP8266 wytrzymuje 5V na RX.
Nadajnik
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial sw(2, 3); // RX, TX
int id=12;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Interfacfing arduino with nodemcu");
sw.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Sending data to nodemcu");
int adc=analogRead(A0);
Serial.print("{\"sensorid\":");
Serial.print(id);//sensor id
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("\"adcValue\":");
Serial.print(adc);//offset
Serial.print("}");
Serial.println();
sw.print("{\"sensorid\":");
sw.print(id);//sensor id
sw.print(",");
sw.print("\"adcValue\":");
sw.print(adc);//offset
sw.print("}");
sw.println();
delay(5000);
}
Odbiornik
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void publishSerialData(char *serialData) {
Serial.println(serialData);
}
void loop() {
//client.loop();
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char bfr[101];
memset(bfr, 0, 101);
Serial.readBytesUntil( '\n', bfr, 100);
//Serial.println(bfr);
publishSerialData(bfr);
}
}
Połączenie w obie strony z Json
Łącząc kody HOW TO SERIAL COMMUNICATION BETWEEN NODE MCU AND ARDUINO z ACROBOTIC napisałem taki program, który używa połączenia szeregowego korzystając z biblioteki ArduinoJson v 6.0 :
Arduino part:
/*
bismillah hir rahman nir raheem
UNO/Nano = Pin 7 & Pin 8
Note: Uno and ESP8266 cross connection
https://github.com/acrobotic/Ai_Tips_ESP8266/tree/master/esp8266_arduino_comm
*/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <millisDelay.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#define rx 7
#define tx 8
SoftwareSerial ArduinoUno(rx, tx); // RX, TX
millisDelay sendIt;
String f, g;
int i, j;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(rx, INPUT);
pinMode(tx, OUTPUT);
ArduinoUno.begin(9600);
sendIt.start(5000);
}
void loop() {
delay(100);
//=============== RX ==============
String content = "";
boolean messageReady = false;
while (messageReady == false) { // blocking but that's ok
while (ArduinoUno.available()) {
content = ArduinoUno.readString();
}
messageReady = true;
}
if (content != "") {
Serial.println();
Serial.println(content);
DynamicJsonDocument doc(1024);
DeserializationError error = deserializeJson(doc, content);
if (error) {
Serial.print(F("deserializeJson() failed: "));
Serial.println(error.c_str());
messageReady = false;
return;
}
serializeJsonPretty(doc, Serial);
Serial.println();
}
//=============== TX ==============
if (sendIt.isFinished()) {
sendIt.repeat();
DynamicJsonDocument doc(1024);
doc["temp"] = 99.99;
doc["hum"] = 88.88;
doc["light"] = 198;
doc["batt"] = 3.33;
serializeJson(doc, ArduinoUno);
Serial.println("Wysłano dane do NodeMCU");
Serial.println();
}
}
ESP8266 part:
/*
bismillah hir rahman nir raheem
ESP8266 = Pin D7 & Pin D8
Note: Uno and ESP8266 cross connection
https://github.com/acrobotic/Ai_Tips_ESP8266/tree/master/esp8266_arduino_comm
*/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <millisDelay.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
millisDelay sendIt;
#define rx D7
#define tx D8
SoftwareSerial NodeMCU(rx, tx); //RX, TX
String f;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
NodeMCU.begin(9600);
pinMode(rx, INPUT);
pinMode(tx, OUTPUT);
sendIt.start(4000);
}
void loop() {
delay(100);
//=============== RX ==============
String content = "";
boolean messageReady = false;
while (messageReady == false) { // blocking but that's ok
while (NodeMCU.available()) {
content = NodeMCU.readString();
}
messageReady = true;
}
if (content != "") {
Serial.println();
Serial.println(content);
Serial.println();
DynamicJsonDocument doc(1024);
DeserializationError error = deserializeJson(doc, content);
if (error) {
Serial.print(F("deserializeJson() failed: "));
Serial.println(error.c_str());
messageReady = false;
return;
}
serializeJsonPretty(doc, Serial);
Serial.println();
}
//=============== TX ==============
if (sendIt.isFinished()) {
sendIt.repeat();
// long i = (700000L);
// f = "z" + String(i);
// NodeMCU.println(f);
//delay(100);
DynamicJsonDocument doc(1024);
doc["z"] = 700000L;
serializeJson(doc, NodeMCU);
Serial.println("Wysłano dane do Arduino");
Serial.println();
}
}
