Informacje:
- Napięcie robocze: 1,8 – 6 V.
- Rozdzielczość temperatury: 0,01 °C
- Dokładność pomiaru temperatury: ± 0,3°C.
- Typ interfejsu: I2C
- Wymiary modułu: 16 x 11 mm.
Biblioteki:
- MicroPython
- https://github.com/targetblank/micropython_ahtx0 // sprawdziłem, działa
- Arduino
- Thinary/AHT10 (github.com) // jeszcze nie sprawdziłem
Połączenie:
Moduły łączymy z płytkami przez I2C
MicroPython:
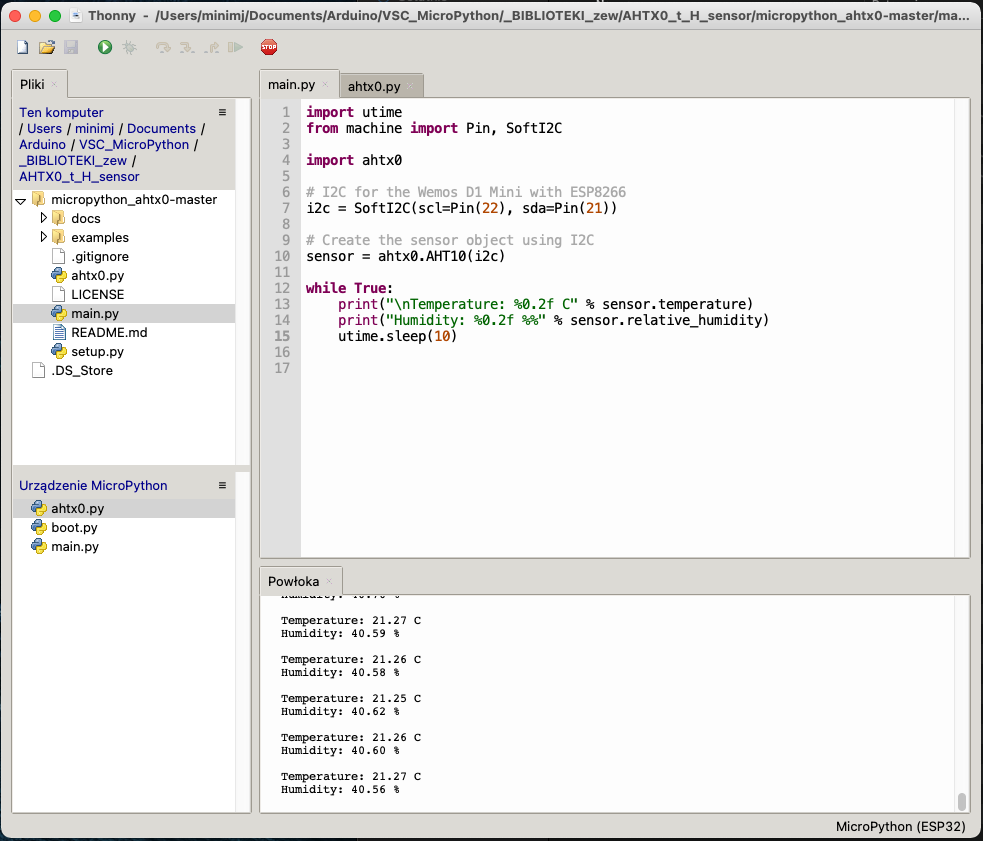
Wspomniana wyżej biblioteka ahtx0.py świetnie współpracuje z ESP32. W programie zmieniłem I2C na SoftI2C (linia 2 i 7). Do ESP32 należy wysłać bibliotekę ahtx0.py i program main.py. Poniżej zrzut z bardzo pomocnego edytora Thonny.
KOD
import utime
from machine import Pin, SoftI2C
import ssd1306Adafruit
import ahtx0
# I2C for ESP32
i2c = SoftI2C(scl=Pin(22), sda=Pin(21))
oled = ssd1306Adafruit.SSD1306_I2C(128,32,i2c)
# Create the sensor object using I2C
sensor = ahtx0.AHT10(i2c)
oled.contrast(0x22)
while True:
# oled.poweron()
oled.fill(0)
# t = str('%0.1f'% sensor.temperature)
t = round(sensor.temperature, 2)
h = round(sensor.relative_humidity, 0)
oled.text('Temp.C: ', 0, 5 )
oled.text(str(t), 60, 5 )
oled.text('Hum.%: ', 0, 20 )
oled.text(str(h), 60, 20 )
oled.show()
print("\nTemperature: %0.3f C" % sensor.temperature)
print("Humidity: %0.3f %%" % sensor.relative_humidity)
utime.sleep(10)
